Understanding Loguytren Problems: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
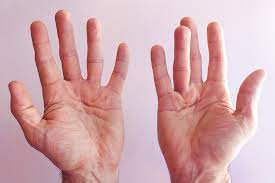
“Loguytren problems” refer to a condition that affects the hands, leading to the thickening and tightening of tissue beneath the skin, primarily in the palm and fingers. Although not widely recognized under this exact name in formal medical literature, the term is often colloquially or mistakenly used in reference to Dupuytren’s contracture, a well-documented hand deformity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what “Loguytren problems” are, what causes them, the symptoms, treatment options, and how individuals can cope with and manage this condition.
What Are Loguytren Problems?
Loguytren problems describe a condition in which the connective tissue under the skin of the palm contracts and thickens over time. This causes one or more fingers (often the ring or little finger) to bend toward the palm and become difficult or impossible to straighten. The condition typically progresses slowly and may lead to significant hand function issues.
This condition is often progressive and irreversible without medical intervention, and it most likely refers to Dupuytren’s contracture, named after French surgeon Baron Guillaume Dupuytren who first described it in the 19th century. However, many people use alternative terms like “Loguytren problems” when searching for information online.
Causes of Loguytren Problems
The exact cause of Loguytren problems is unknown, but several contributing factors have been identified:
1. Genetics
A family history of Loguytren problems or Dupuytren’s disease significantly increases the risk. The condition is more prevalent in individuals of Northern European descent.
2. Age
It typically occurs in individuals over the age of 40, with incidence increasing as people age.
3. Gender
Men are more likely to develop Loguytren problems than women, and in men, the condition is generally more severe.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to a higher risk. These habits may impair blood circulation and tissue health.
5. Medical Conditions
Diabetes, epilepsy, and liver disease have all been associated with a higher incidence of connective tissue disorders like Loguytren problems.
Symptoms of Loguytren Problems
The symptoms associated with Loguytren problems tend to develop slowly over several years and may vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
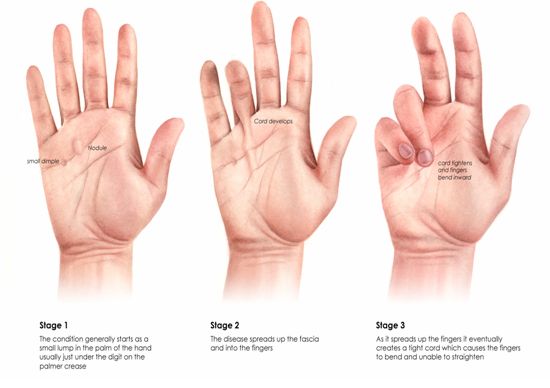
- Nodules: Small lumps or nodules form in the palm, usually near the base of the fingers.
- Pits: Depressions or indentations in the skin of the palm may appear.
- Cord Formation: Tight cords of tissue may develop under the skin, eventually pulling the fingers downward.
- Contractures: Permanent bending of one or more fingers, usually the ring or little finger.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty in extending fingers, grasping objects, or performing daily tasks such as typing or buttoning a shirt.
Diagnosing Loguytren Problems
A diagnosis of Loguytren problems is primarily clinical, based on the symptoms and physical appearance of the hand. A doctor or hand specialist will typically:
- Examine the palm and fingers for nodules or cords.
- Conduct a tabletop test: the patient is asked to lay their hand flat on a table. If they cannot do this, it may indicate a contracture.
- Evaluate range of motion and grip strength.
Imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs are rarely required unless other underlying conditions are suspected.
Treatment Options for Loguytren Problems
There is no cure for Loguytren problems, but various treatments can slow progression and improve function. The appropriate treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
a. Needle Aponeurotomy
A minimally invasive procedure where a needle is used to puncture and break the cords of tissue. It has a quick recovery time but may not be suitable for all cases.
b. Collagenase Injections (Xiaflex)
An FDA-approved enzyme injection that dissolves the tight cords, allowing the fingers to be straightened. It is effective but may have side effects like bruising or swelling.
c. Physical Therapy
Exercises and stretching may help maintain range of motion in the early stages but won’t reverse contractures.
d. Splinting
Splints can help in early stages to maintain finger extension, although their effectiveness is debated.
2. Surgical Treatments
a. Fasciotomy
A surgical procedure where the contracted tissue is cut to release tension. It is typically used when non-surgical methods are ineffective.
b. Subtotal or Total Fasciectomy
Removal of the affected tissue in the palm and fingers. This is more invasive and requires a longer recovery but may offer longer-lasting results.
c. Dermofasciectomy
In severe or recurrent cases, the affected skin and tissue are removed, and a skin graft is applied.
Living with Loguytren Problems
For many, Loguytren problems progress slowly and may not require treatment for years. However, for others, the condition can interfere with work, hobbies, and daily life. Here are ways to manage:
- Stay Active: Use your hands frequently to maintain mobility and strength.
- Monitor Changes: Regularly assess your hand for new nodules or worsening curvature.
- Seek Early Treatment: The earlier you intervene, the better the outcome.
- Supportive Devices: Adaptive tools can assist with daily tasks.
- Hand Therapy: Regular therapy sessions can delay contracture progression.
Risk of Recurrence
One of the most frustrating aspects of Loguytren problems is the high risk of recurrence. Even after successful treatment, the disease may return in the same or other fingers. Surgical methods tend to offer longer relief, but recurrence is still common. Therefore, ongoing monitoring and early intervention are key.
Psychological Impact of Loguytren Problems
Chronic conditions like Loguytren problems can have a psychological toll. Many people experience:
- Frustration due to limitations in hand function
- Anxiety about disease progression
- Embarrassment over hand appearance
- Depression, particularly when the condition interferes with hobbies or work
Support groups, therapy, and open communication with healthcare providers are essential components of holistic care.
Future Treatments and Research
Ongoing research is looking into more effective treatments for Loguytren problems, including:
- Gene therapy to target the root cause
- Biologic drugs to reduce tissue fibrosis
- Improved enzyme formulations for less invasive options
Clinical trials continue to seek better outcomes for individuals living with this challenging condition.
Conclusion
Loguytren problems, often a misnomer or colloquial term for Dupuytren’s contracture, present significant challenges for those affected. Though the condition is not life-threatening, it can substantially impair quality of life and hand function. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and pursuing appropriate treatment are crucial for managing the disease. With advancements in medical science and a proactive approach to care, individuals facing Loguytren problems can maintain hand functionality and enjoy a more active and independent life.







